
|

|
No. 84 October 2012 |
| |
Basic Science
Mystery of Brain Vascular Network Formation Revealed
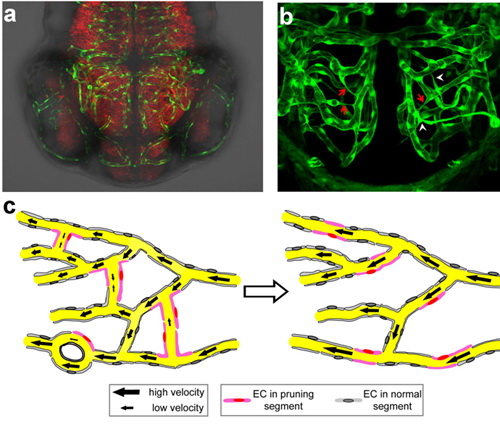
Dr. Du JiulinĄ¯s lab at the Institute of Neuroscience, CAS, published a research article on Aug. 14, 2012, entitled "Haemodynamics-Driven Developmental Pruning of Brain Vasculature in Zebrafish" in PLoS BIOLOGY. In this study, zebrafish was used as a simple vertebrate animal model and multi-disciplinary approaches adopted, the authors found that changes of brain blood flow drove vessel pruning via lateral migration of vascular endothelial cells, leading to the simplification of 3-D brain vascular network and efficient routing of artery-venous blood flow in the developing brain. This study reveals an essential role of vessel pruning in brain vascular development and provides a novel insight into how vessel segments are pruned. It will spark further investigation in the vascular research field. Considering the importance of the vasculature system in cancer maintenance and metastasis, understanding vessel pruning may offer a new strategy for cancer therapy. This work was highlighted by PLoS BIOLOGY, NAURE, and Faculty of 1000. This work was carried out by Chen Qi, graduate student, Jiang Luan, post-doctoral fellow, and Li Chun and Bu Jiwen, technicians under the supervision of Dr. Du Jiulin in collaboration with Drs. David Cai and Hu Dan in the Department of Mathematics and Institute of Natural Sciences, Shanghai Jiaotong University.
New Way to Cure Metabolism Diseases
A latest research result published online in Cell Metabolism on Aug. 3, 2012, convincing the recent achievement by Dr. Song BaoliangĄ¯s and Li BoliangĄ¯s groups from the Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, CAS. This research discovered the mechanism for an ubiquitin ligase gp78 regulating the lipid metabolism, which offers a novel means to cure a series of metabolic diseases such as obesity. Although cholesterol and other lipid molecules have essential biological functions, excessive cholesterol can result in atherosclerosis, which may lead to severe diseases such as coronary heart disease and stroke. Thus, lipid levels must be regulated tightly and precisely. Ubiquitin ligases are enzymes that cause the attachment of ubiquitin (a small protein, it can label proteins for destruction) to target proteins for degradation by the proteasome. As an ubiquitin ligase, gp78 can mediate the degradation of key proteins involved in cholesterol homeostasis. Since liver is the major organ for lipid metabolism, Dr. Song BaoliangĄ¯s and Li BoliangĄ¯s groups used a mouse model, of which hepatic gp78 was specifically deleted to investigate the physiological function of gp78. Liu Tongfei, Ph.D student and his colleagues discovered that hepatic gp78-deficient mice were leaner with less fat and significantly resistant to diet-age-induced obesity and glucose intolerance. The molecular mechanisms underlying these phenotypes that are functioning mainly due to the suppression of lipogenesis and the elevation of expenditure of massive glucose, fatty acids and other nutritional materials. Further, this study not only discovered the relationship between lipid and energy metabolism, but also indicated that gp78 is a promising target for ameliorating and curing of obesity, diabetes and other metabolic diseases.
copyright © 1998-2015
CAS Newsletter Editorial Board: 52, Sanlihe Road, Beijing 100864,
CHINA
Email: slmi@cashq.ac.cn