
|

|
No. 83 August 2012 |
| |
Bioscience
Potential New Mechanism for Enhancement of HIV-1 Transmission Revealed
Epithelial cells are the main targets of HSV-2 while HIV-1 preferentially infects CD4+ T cells. Epidemiological studies indicate that HSV-2 infection increases the risk of HIV-1 acquisition and transmission, but the underlying mechanism remains elusive. Dr. Hu Qinxue¡¯s group at the Wuhan Institute of Virology demonstrates that HSV-2 infection induces CXCL9 expression in human cervical epithelial cells by activation of p38-C/EBP-¦Â pathway through promoting the binding of C/EBP-¦Â to CXCL9 promoter, which may recruit activated CD4+ T cells to mucosal HSV-2 infection sites and potentially increase the risk of HIV-1 sexual transmission. Their findings published in the Journal of Immunology, 2012 Jun 15; 188 (12):6247-57). Faculty of 1000 has recently selected and evaluated the result, pointing out ¡°This relevant manuscript provides a potential new mechanism underlying the herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2)-mediated enhancement of mucosal transmission of HIV-1¡±.
New Regulatory Roles of Transcription Factors Revealed
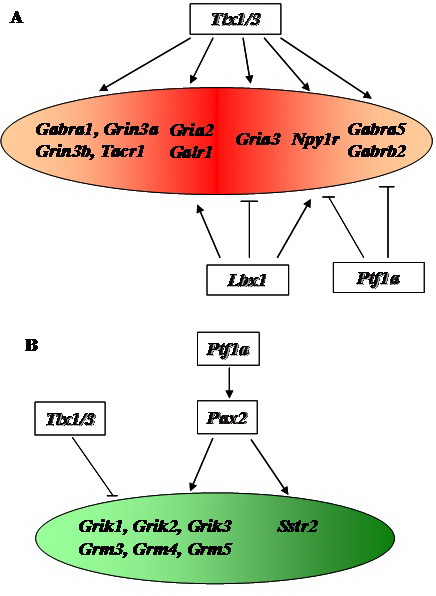
Under the supervision of Dr. Cheng Leping, graduate students Guo Zhen, Zhao Congling, and Huang Menggui from the Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences found that a distinct set of neurotransmitter and peptide receptor genes were preferentially expressed in glutamatergic neurons in the dorsal spinal cord by means of in-situ hybridization and immunostaining. By examining the phenotypes of the knockout mice, they found that deletion of transcription factors Tlx1 and Tlx3 resulted in the loss of expression of these receptor genes. Furthermore, they obtained genetic evidence that transcription factors Lbx1 and Ptf1a played roles in controlling the expression of some of these receptor genes. They also found that another distinct set of neurotransmitter and peptide receptor genes were mainly expressed in GABAergic neurons in the dorsal spinal cord, and that their expression required the presence of transcription factor Ptf1a. Additionally, transcription factors Pax2 and Tlx1/3 were required for the proper expression of these receptors in GABAergic neurons. These findings indicate that the key transcription factors for fate determination of glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons in the dorsal spinal cord also coordinate the expression of distinct sets of neurotransmitter and peptide receptor genes, which are enriched in glutamatergic or GABAergic neurons. This study provides some new information for understanding of the mechanism underlying neuronal specification and neural circuit formation. Neuroscience published online their achievement on June 20, 2012.
copyright © 1998-2015
CAS Newsletter Editorial Board: 52, Sanlihe Road, Beijing 100864,
CHINA
Email: slmi@cashq.ac.cn