
|

|
No. 77 August 2011 |
| |
International Cooperation
CFOSAT: New Insights into Sea State
A joint project of the China National Space Administration (CNSA) and the Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNES), CFOSAT (China-France Oceanography Satellite) is now entering its substantial phase. An overall test for the sample prototype (electrical devices) of microwave scatterometer (SCAT) and relevant test was completed on July 23rd. For the time being, production of some quasi- authenticated products is underway and follow-up tests are being arranged. The satellite¡¯s major goal will be to determine the direction, amplitude and wavelength of surface waves in order to characterize what oceanographers call ¡°sea state¡±. For this purpose, two major effective loads are included in this project: the Chinese SCAT instrument, a conical-scanning scatterometer designed to measure wind speed, which will operate alongside the SWIM (Surface Wave Investigation and Monitoring), a highly innovative measuring instrument, which is developed by Thales Alenia Space in Toulouse.

Find More and Deeper into the Space
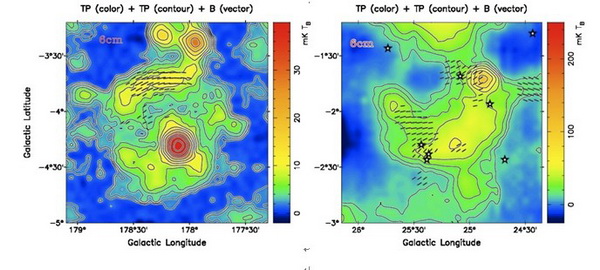
A Sino-German ¦Ë6 cm (5 Ghz frequency) polarization survey of the Galactic plane was conducted by using the 25-meter radio telescope of Xinjiang Observatory. The National Observatory, in cooperation with Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy, spent 10 years to complete the surveys. The polarized emission of the Galaxy and physical properties of scores of celestial bodies has been measured, and the two large supernovas remnants were recently discovered. Dr. Han Jinlin, Chief Research Fellow of Compact Object and Diffused Medium Research Group of the National Astronomical Observatory of China, and Prof. Richard Wielebinski, Director of the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy (Honorary Director) agreed in 2001 to jointly study the magnetic field of the Galaxy. Under the strong support and assistance of Xinjiang Observatory, Sino-German Partner Group has taken enormous efforts for 4500-hour observation to cover 2200-square degree of the galactic plane within the Galactic longitude between 10 degree and 230 degree and galactic latitude minus 5 degree to plus 5 degree. So far, it is the largest area of the Galactic plane surveyd for polarization by using the ground radio telescope with the highest observation frequency. Using the new survey data, the group discarded two objects which were previous wrongly identified as supernovas remnants G166.2+2.5 (OA 184) and G192.8-1.1 (PKS 0607+17). After careful analysis of the survey data, the group discovered two supernovas¡¯ remnants - G178.2-4.2 and G25.1-2.3, both have a size larger than I degree. It is the first time for the Chinese to discover the new supernova remnants using their domestic radio telescope and their own observational data. So far, Sino-German project has completed and published 23 papers, mostly in the international journal Astronomy and Astrophysics, of which two papers were recommended to be the highlights by the chief editors.
copyright © 1998-2015
CAS Newsletter Editorial Board: 52, Sanlihe Road, Beijing 100864,
CHINA
Email: slmi@cashq.ac.cn