
|

|
No.63 April, 2009 |
| |
Basic Science
New Deformation Mechanisms of Titanium Alloy Revealed
The Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science, the Institute of Metal Research, CAS, recently made a significant progress in the research on micro-mechanism of the nonlinear elasticity deformation of a new-type multi-function titanium alloy. The research team led by Sui Manling of the Solid Atomic Imaging Division, together with Yang Yue and Hao Yulin research team of the Engineering Alloy Division demonstrates reversible movement of dislocation loops generated from nanodisturbances in a titanium alloy. High resolution transmission electron microscope observations during an in situ tensile test found three reversible deformation mechanisms, nanodisturbances, dislocation loops and martensitic transformation, that are triggered in turn with increasing applied stress. All three mechanisms contribute to the nonlinear elasticity of the alloy. The experiments also revealed the evolution of the dislocation loops to disclination dipoles that cause severe local lattice rotations. Their work will not only help with profound understanding of the nature of nonlinear elasticity deformation of this new-type multi-function titanium alloy, but also provides knowledge basis for the design of new super-elasticity metal materials. The results were published online on Jan. 30 issue of the Physical Review Letters.
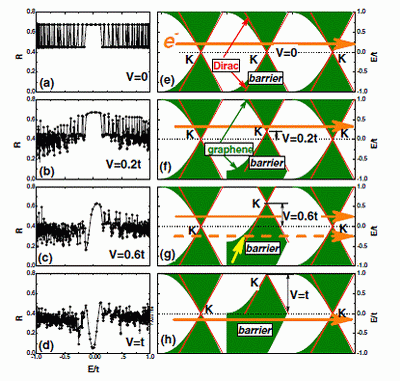
New Progress on Disordered Graphene Research
Recently, Liu Wuming Research team of the Institute of Physics/Beijing National Laboratory for Condensed Matter Physics, CAS, made a significant progress in the research of the localization and the Kosterlitz-Thouless transition of disordered graphene. They found that states near the Dirac points are localized for sufficiently strong disorder (therefore inevitable intervalley scattering) and the transition between the localized and delocalized states is of Kosterlitz-Thouless type. This new research work is of great significance to further understand the novel nature of disorder grapheme. Their results were published on Mar. 10 issue of the Physical Review Letters 102, 106401(2009).
copyright © 1998-2010
CAS Newsletter Editorial Board: 52, Sanlihe Road, Beijing 100864,
CHINA
Email: slmi@cashq.ac.cn