
|

|
No. 74 February 2011 |
| |
Applied Technology
Micro-and Nanoscale Metallic Glassy Fibers Prepared
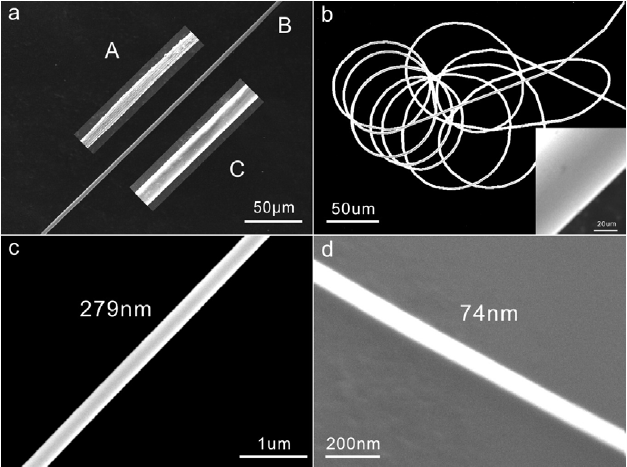
When bulk materials are made into micro and nano scale fibres, there will be attractive improvement of structural and functional properties, even unusual experimental phenomena. The main drawback of various applications of metallic fibres is poor ability of present fabrication methods for controlling their dimensions and surface properties. Metallic glassy fibres (MGFs) are desired because of unique mechanical and physical properties and glass-like thermoplastic processability of metallic glasses.
Recently, Wang Weihua¡¯s group in the institute of physics developed a synthetic route for production of micro to nano scale MGFs (the diameter ranges from 100 m to 70 nm) by driving bulk metallic glass rods in their supercooled liquid region via superplastic deformation. Compared with existing metallic fibres, the MGFs have precisely designed and controlled properties and size, high structural uniformity and surface smoothness, and extreme flexibility. Remarkably, the method is simple, efficient and the cost is low, and the MGFs can be continuously prepared by the method. Furthermore, the MGFs circumvent brittleness of metallic glasses by size reduction. They proposed a parameter based on the thermal and rheological properties of MG-forming alloys to control the preparation and size of the fibres. The MGFs with superior properties might attract intensive scientific interest and open wide engineering and functional applications of glassy alloys (Related results were published in Adv Eng Mater12, 1117 (2010)).
First MW High-current Ion Source
The first powerful high-current positive ion source recently got through its vacuum test, insulation test, plasma generator¡¯s power supply system test, and static high voltage loading test, obtaining the first plasma at arc current of 900A for two seconds. This is a big step forward in EAST neutral beam injection (NBI) auxiliary heating project, a four-year national large-scale scientific project. The filament power supply system (6V, 2.2kA), arc power supply system (50V) and suppression power supply system (-4kV) were applied during the static high voltage loading test, with power output 50kV and pulse width 500ms. During the development of high-current ion source, the team established a close cooperation relationship with many domestic and international institutes, including Southwestern Institute of Physics (SWIP), General Atomics (GA) in the United States, National Institute for Fusion Science (NIFS) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in Japan, Max Planck Institute of Plasma Physics (IPP) in Germany, and Budker Institute of Nuclear Physics (BINP) in Russia. Through the collaborations, NBI team constructed the precise parts of megawatts positive ion source and mastered advanced manufacturing technologies for ion source, including solder formulation, loading fixtures, vacuum furnace welding process, and quality testing technology. Meanwhile, power supply system for plasma generator, measurement and data acquisition system, high voltage power supply system, the snubber system have been also built. All such work has laid a good foundation for the development of the powerful neutral beam injection system for EAST. "This is just a phaseal advance for EAST NBI", said Prof. Hu Chundong, head of NBI team modestly. "More challenges are ahead of us. We will brave them one by one as we are a very young, give-it-all team."
copyright © 1998-2015
CAS Newsletter Editorial Board: 52, Sanlihe Road, Beijing 100864,
CHINA
Email: slmi@cashq.ac.cn