

The nanostructured carbon catalysts such as nanotube, nanodiamond, and graphene as an important metal-free catalyst have demonstrated excellent catalytic performance in various catalytic processes comparable or even better than the conventional metal catalysts. Oxygen, nitrogen, boron, and sulfur are the most important surface functional groups on the nanostructured carbon catalysts which have a significant influence on the catalytic capability. The deep understandings of the tunable effect of surface functional groups have apparent importance to the optimization and development of the nanostructured carbon catalysts.
In the past five years, researchers from the Catalysis and Energy Materials Division of the Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IMR, CAS) have employed first principle calculations and quantum chemistry methods to understand the chemical properties of the surface functional groups including oxygen, nitrogen, boron, and sulfur, as well as their catalytic role in reactions such as dehydrogenation of alkanes, CO oxidation, oxygen reduction reaction, and selective hydrogenation.
The general principle and working mechanism is also proposed.
1.The nucleophilic ability of oxygen groups and the acid/base property of nitrogen groups
Various oxygen groups such as quinone, ketone, and phenol can be anchored onto nanostructured carbon materials by using HNO3 treatment. To correctly distinguish the different reactivities of various oxygen groups or the same group under different chemical environments is a difficult task. Due to the co-existence of the various groups, it is very hard to reveal the difference. By using Fukui function, for the first time the nucleophilic ability of various oxygen groups are quantitatively described. The computational results can help the following experimental work to unambiguously identify the active site (Chemistry - A European Journal 2014, 20, 7890-7894).
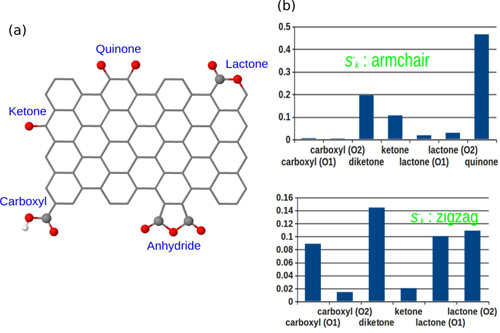
Figure 1. (a) oxygen functional groups on the nanostructured carbon catalysts (b) nucleophilic ability of the oxygen groups (Image from IMR)

Figure 2.ODH of propane reaction process at single ketone site (Image from IMR)
The nitrogen functional groups can significantly increase the basicity of the carbon materials. Pyridine, pyrrole, quantenary, and graphitic nitrogen are the most often observed groups on the carbon materials. To identify the strongest basic site, the proton affinity and acid dissociation constant are calculated. The results indicate that the pyridine nitrogen is the strongest basic group. This conclusion will shed light on further base catalysts applications (Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.2015, 17, 6691-6694).
2.The active site, reaction pathway, and mechanism of oxidative dehydrogenation of short alkanes
The oxidative dehydrogenation (ODH) of short alkanes is one of the most successful applications of the nanostructured carbon catalysts. The first principle calculations for the first time reveal the complete reaction pathway of the ethane ODH (J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 5287-5294). The calculations indicate a new mechanism of the active site regeneration. The oxygen removal energy is revealed to be an effective descriptor for the activity. Furthermore, the calculations indicate that the carbon atom which is adjacent to the oxygen groups can also be reactive to C-H bond activation. This suggests that a single ketone group can be the active site in ODH (Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 11016-11019). The origin of the activity is deduced to be from the reduced aromaticity (Chemistry – An Asian Journal 2016, 11, 1668-1671).
3.The reaction mechanism of direct dehydrogenation reaction
Nanodiamond has an excellent catalytic performance in the direct dehydrogenation reaction with good selectivity and stability. It not only has a better performance than the conventional metal catalysts but also outperforms the other carbon catalysts such as nantobue. By using first principle calculations, the unique relation between sp2@sp3 core-shell structure and the catalytic performance is revealed from structure analysis, C-H activation barrier, charge transfer, and size effect. The calculation results lay out a solid base for the further optimization of the carbon catalysts in the direct dehydrogenation reaction (ACS Catalysis 2017, 7, 3779-3785).
4.The novel hydrogenation catalyst
Hydrogen is one of most important elements in the catalytic reaction. Conventionally, the hydrogen activation is catalyzed by the transition metal. By using Frustrated Lewis Pair concept, a novel hydrogenation catalyst, boron and nitrogen codoped bilayer graphene, is computationally designed. The calculations indicate the novel codoped catalysts have comparable performance with the noble metal catalysts (Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 11120-11124). Furthermore, researchers choose the selective hydrogenation of cinnamaldehyde and validate the method to increase the product selectivity (ChemCatChem 2014, 6, 3246-3253).
5.The tunable effect of the surface functional group on the supported metal catalysts
Several different configurations of boron and nitrogen doped carbon nanotube are constructed. Due to the electronegativity difference, boron and nitrogen have opposite effects on the electronic structure of supported single Au atom. The charge analysis reveals that electron is from Au in the support on the nitrogen doping; and from support to the Au on the boron doping. The different charged state of Au directly influences the interactions between catalysts and reactants. CO is more stable on the nitrogen doped support and O2 is more stable on the boron doped support. This directly leads to the different reaction mechanisms. Besides the conventional LH of an ER reaction mechanism, a novel tri-molecule reaction mechanism is also found. This study brings a unique insight into the tunable effect of the surface functional groups on the support (J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 16653-16662). Moreover, the catalytic role of the defects including mono vacancy, di-vancancy, and Stone-Wales defect is also explored for the supported single Au atom. Through the comparison, the curvature effect is also revealed (Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 22344-22354).
6.The general principle of the tunable effect of surface functional groups
The calculations indicate that the nitrogen groups can increase the nucleophilic ability of the oxygen and enhance the desorption of the formed olefin in the dehydrogenation reaction which increases the selectivity(Chem. Asian J. 2013, 8,2605-2608). In contrast to nitrogen, boron has one less valence electron than carbon, and therefore boron doping will create a hole state. The calculations indicate that the boron doping can activate the oxygen molecule and produce the reactive oxygen species which can catalyze methane conversion (Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2013, 117, 17485-17492). Through high throughout calculation, BEP rule is found to be valid for the doped carbon catalysts in the dehydrogenation reaction. And the breaking bond distance shows a linear relation with the reaction barrier (Nanoscale 2015, 7, 16597-16600).
Since 2013, the research team has published 29 papers in SCI journals such as ACS Catalysis, Nanoscale, J. Mater. Chem. A, and Chem. Comm. In particularly, the paper of the tunable effect of dopants on support to the single Au atom was selected as a 2017 “HOT Article” by J. Mater. Chem. A. Recently, part of the work entitled with “Oxidative dehydrogenation reaction of short alkanes on the nanostructured carbon catalysts: a computational account” was accepted as Feature Article by Chem. Communications. This work is supported by NSFC, the Institute of Metal Research, Sinopec, and the Guangdong Supercomputing Center.
Source: Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences
For more information, please contact:
Prof. Su Dangsheng
E-mail: dssu@imr.ac.cn