

Ferroelectric flux-closures, which exhibit closed head-to-tail continuous electric dipoles, are very promising in high density storage, because data storage in these domain patterns may avoid the problem of “cross-talk”. For the purpose of the data bits to be addressable, nanoscale flux-closures should be periodic.
In the new issue of Nano Letters on November 16, 2017, a research team led by Prof. Ma Xiuliang and Prof. Zhu Yinlian from the Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IMR, CAS) published their recent achievement in establishing the phase diagram of the layer-by-layer two-dimensional flux-closure arrays versus the thickness ratio of adjacent ferroelectric PbTiO3 films.
Based on the one-dimensional flux-closure array (Science, 2015) discovered by the team, they recently artificially produced a series of PbTiO3/ SrTiO3 multilayers grown on GdScO3 (001) pc substrate with multiple periodicities.
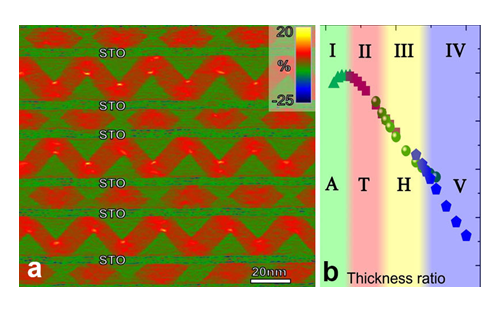
Figure: Identification of 2D regularly arranged vertical and horizontal flux-closure quadrants. (a) Out-of-plane lattice strain maps of the PbTiO3/ SrTiO3 multi-layers; (b) Total energy density in the multilayered PbTiO3/ SrTiO3 systems as the function of the thickness ratio of adjacent PbTiO3 layers. (Image by IMR, CAS)
By tuning the thickness ratio of adjacent PTO layers, they have obtained two configurations of the flux-closure array: one feature with 180° domain walls perpendicular to the interfaces and another with 180° domain walls parallel to the interfaces.
With methods of aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopic imaging and phase field modeling, they have established the phase diagram of the two-dimensional flux-closure arrays versus the thickness ratio of adjacent PbTiO3 films, in which energy competitions play dominant roles.
The growth of these flux-closures makes a great step toward the realization of ferroelectric nano-scale devices with exotic properties.
For more information, please contact:
1, Dr. Ma Xiuliang
E-mail: xlma@imr.ac.cn.
2, Dr. Zhu Yinlian
E-mail: ylzhu@imr.ac.cn.
Shenyang National Laboratory for Materials Science
Institute of Metal Research
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Source: Institute of Metal Research, CAS