

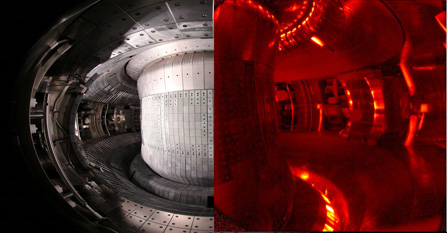
The interior of the donut-shaped EAST and an infrared image when EAST is discharged. Deuterium plasma is confined in this chamber by strong magnetic fields, where it fuses into heavier nuclei. The temperature within can reach as high as 50 million degrees Celsius, with an external temperature of superconducting magnet as low as 269 degree Celsius below zero. (Image from Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, CAS)
Fusion reaction is how stars generate energy. The reaction usually happens in a plasma (of deuterium and tritium) heated to millions of degrees. Outside of a star, however, the way to confine the plasma at these temperatures while the reactions take place is to use magnetic fields. Here comes EAST from the Far East.
On the night of July 3rd, EAST made an exciting advance in achieving a stable 101.2-second steady-state high confinement plasma, setting a world record in long-pulse high mode operation.
The Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) fusion research facility, nicknamed "artificial sun", conducts fundamental physics and engineering research on advanced tokamak fusion reactors with steady state and high performance and provides a scientific base for future reactor design and construction. It is the first tokamak to employ superconducting toroidal (long way) and poloidal (short way) magnets. It aims for plasma pulses of up to 1,000 seconds.
The 100s record results essentially from effective control of the divertor (waste removal device)’s target heat load and tungsten impurity influx and maintenance of the center chord average electron density at > 50 percent of the Greenwald density limit. In tokamaks, exceeding the Greenwald limit typically leads to a disruption.
EAST has been widely considered as a group of experiment-driven rather than theory-driven facilities, consisting of six major sub-systems, namely Toroidal Field Magnet, Poloidal Field Magnet, Thermal Shield, Vacuum Vessel, Cryostat and Auxiliary Heating.
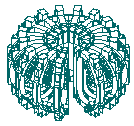
Toroidal field magnet confines magnetic field parallel to lines of latitude.
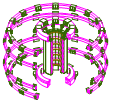
Poloidal field magnet confines magnetic field in the direction towards the poles.

Vacuum vessel is a hermetically sealed steel container that houses the fusion reactions and acts as a first safety containment barrier.
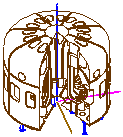
Thermal shield is a layer to reduce radiation heating in the vessel.
Cryostat is the stainless steel structure surrounding the vacuum vessel and the superconducting magnets, in order to provide a super-cool vacuum environment.(Images from Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, CAS)
All the plasma parameters, including recycling, particle and heat fluxes, reached true steady-state after 20s -- the wall saturate time for the W divertor -- and maintained stability to the end of discharge.
Chief Operator Gong Xianzu shared the good news and his excitement with EAST partners at home and abroad at midnight via social media.
Gong has witnessed every advance made on the machine as well as its setbacks since his first operation of EAST in 2006. This breakthrough, he said, indicates EAST will "continue to play a key role on both physics and engineering fronts of steady-state operation, and has significant scientific implications for the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER) and the future China Fusion Engineering Test Reactor (CFETR)".
"It is a success of joint efforts," said Gong. The EAST team has worked together with their collaborators at home and abroad over the past decade to solve a series of key technical and physical issues closely related to the steady-state operation, and carried out in-depth scientific research on integrated operation scenarios with effective coupling of multi-scale physical processes.
The EAST 2017 experimental campaign will continue for about one more month and the second round of experiments will start in autumn of this year.
Source: Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, CAS