

Lead article

|

|

|
celebrate the completion of FAST¡¯s main construction work on July 3. Installation work on the reflector began back in August 2015 and, after 11 months, 4,273 triangular segments and 177 specially shaped segments were fixed in a unique structure of thousands of steel cables, nodes and driving cables, tied to actuators on the ground to change from a spherical to a parabolic surface. The idea of building such a telescope was first proposed in 1994 and, after a decade of site surveying, Chinese scientists found a nearly perfect spot in Dawodang, Kedu Town in southeastern China¡¯s Guizhou province, known for its karst formations and mountains that naturally shield against radio frequency interference. Then, the project got Chinese government |
approval in 2007 and is expected to be completed 5-1/2 years. The total cost is estimated at 1.15 billion yuan ($180 million). The general engineer of FAST, Nan Rendong, says, ¡°FAST will allow Chinese astronomers to work towards many goals,such as surveying the neutral hydrogen in the Milky Way,detecting faint pulsars, and listening to possible signals fromother civilizations. It¡¯s time for China to have its own big telescope.¡± Over the next couple of months, the FAST team will do testing and debugging to make sure the telescope works, according to Wang Qiming, head of the reflector system and general technologist for the project, with the official completion date set for late September, and the telescope¡¯s first data expected to arrive around that time. |
Hot Issue

International Cooperation

Research Progress
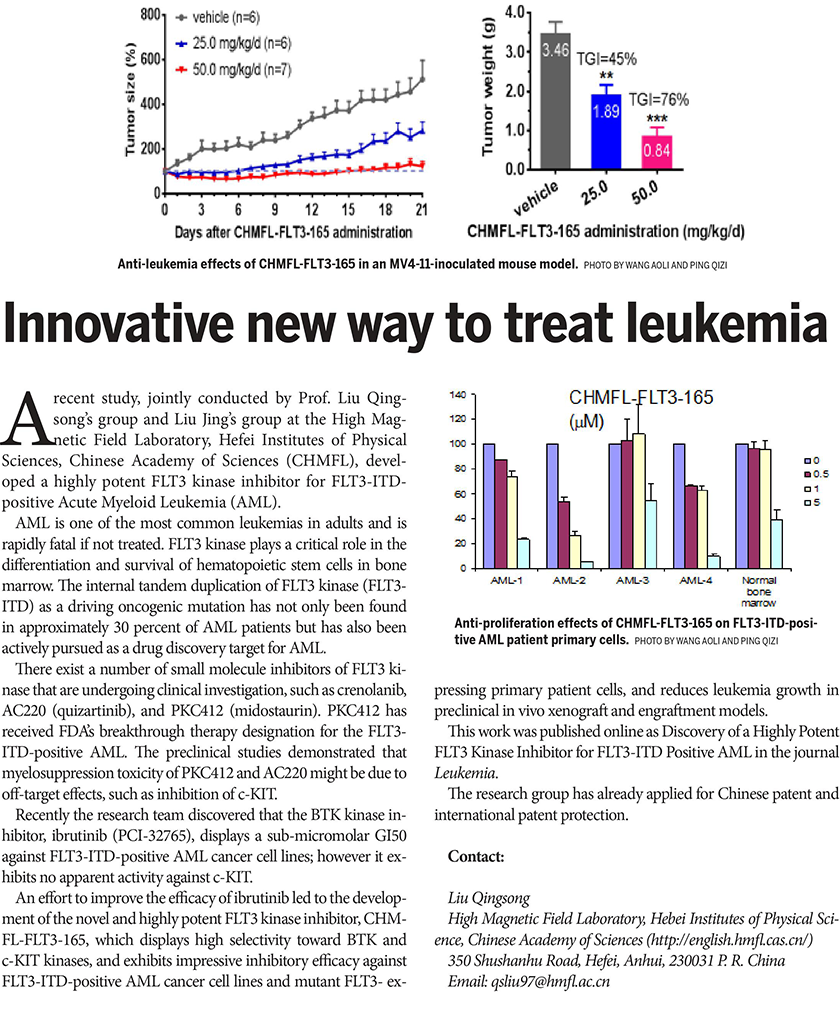
Research Progress

Science Story

News in Brief
